As with all B vitamins, B5 helps the body break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins so that your body can use them for energy and rebuilding tissues, muscles, and organs.
WHERE IT IS FOUND
Pantothenic acid is widely available in food, but it is lost in processing, such as canning, freezing, and milling. For example, whole grains are a reliable source of vitamin B5, but milling can remove up to 75 % of the B5 content. To ensure adequate intake, you should eat foods fresh rather than refined. As with all water-soluble vitamins, vitamin B5 is lost when food is boiled.
Vitamin B5 is soluble in water and is excreted in the urine. Your body does not store it and you need to consume it every day to replenish supplies.
It is widely found in both animals and plant products.
• Meat: Beef, pork, chicken, turkey, duck (especially animal organs e.g., liver and kidney)
• Fish: Salmon, lobster, and shellfish.
• Grains: Whole-grain bread and cereals.
• Dairy products: Milk, milk products, yogurt, egg yolk.
• Legumes: Lentils, split peas, and soybeans.
• Vegetables: Avocado, broccoli, mushrooms, sweet potatoes, corn, cauliflower, kale, and tomatoes.
• Other sources of vitamin B5 include Brewer’s yeast /Peanuts / Sunflower seeds /Wheat germ /Royal jelly /Oatmeal
FUNCTIONS
Vitamin B5 has many essential functions. These include:
- converts food into glucose
- synthesizes cholesterol
- forms sex and stress-related hormones
- forms red blood cells
- Synthesizes coenzyme A:
Coenzyme A is involved in the synthesis of fatty acids and is important for converting foods into fatty acids and cholesterol.
It is also needed for the creation of sphingosine, a fat-like molecule that helps deliver chemical messages inside the body’s cells. Also, the liver needs it to metabolize some drugs and toxins safely. - Digestive system: It helps maintain a healthy digestive system and assists the body in using other vitamins, especially vitamin B2.
- Skincare: Some studies have shown that vitamin B5 works as a moisturizer on the skin and enhances the healing process of skin wounds.
- Cholesterol and triglycerides: Some studies suggest that vitamin B5 intake can help lower cholesterol and levels of blood triglycerides or fats.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Some researchers have found that people with rheumatoid arthritis have lower levels of vitamin B5, but more evidence is needed to confirm these results.
DEFICIENCY
It’s rare to have a vitamin B5 deficiency. Only people who are malnourished will have a B5 deficiency. According to the Mayo Clinic, vitamin B5 deficiency is unlikely to cause any medical problems by itself. However, people with a B5 deficiency are often experiencing other vitamin deficiencies at the same time. Symptoms of a B5 deficiency are likely to include:
- headache
- fatigue
- irritability
- impaired muscle coordination
- gastrointestinal problems Symptoms go away once you start getting enough vitamin B5.
SIDE EFFECTS
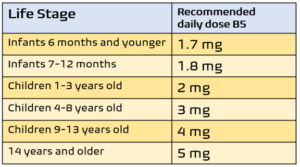
Pantothenic acid is LIKELY SAFE for most people when taken by mouth in appropriate amounts. The recommended amount for adults is 5 mg per day. Even larger amounts (up to ten grams) are safe for some people. But taking larger amounts increases the chance of having side effects such as diarrhea.
RECOMMENDED DAILY DOSE